Advanced Filtering
Tutorial
The Advanced Filtering API allows you to use arbitrary filters to find Leads or Contacts with specific attributes.
To use the Advanced Filtering API, make a POST request to /api/v1/data/search/
with your JSON filters in the request body. Let’s consider a simple example of
finding all Contacts with CEOs you have on file in Close. The example POST
request data with the query would look like this:
{
"query": {
"type": "and",
"queries": [
{
"type": "object_type",
"object_type": "contact"
},
{
"type": "field_condition",
"field": {
"type": "regular_field",
"object_type": "contact",
"field_name": "title"
},
"condition": {
"type": "text",
"mode": "full_words",
"value": "CEO"
}
}
]
}
}The request consists of a top level "and" query which combines two constraints on what would be returned:
- An
object_typequery that tells the API that you’re interested in finding Contacts. - A
field_conditionquery that asks for Contacts that have a title value containing a word"CEO".
Every query has a "type" that distinguishes the way you filter through objects.
The first part of the example query is "type": "object_type". It specifies
that you only want objects of type Contact returned in the response.
The second part of the example query is "field_condition". Field condition
queries specify the field you want to match against (in this case "title"),
and the values you want to match it to (i.e. "CEO").
The field in this example is a "regular_field" named "title" on a
"contact" object. There can be other kinds of fields as well, like
Contact Custom Fields.
The field condition here is a simple "text" condition. It matches against the
text "CEO", so any contact that have a title containing word "CEO" will be
returned.
Here’s an example response:
{
"data": [
{
"__object_type": "contact",
"id": "cont_PtENYt1P6sRWkcnqoGnIj6hcZammGPdVbTXJWqdTvpV"
},
{
"__object_type": "contact",
"id": "cont_HjTcJFiNli2AKf5fioygQDVSpA9nJILI9SkKv3nBk0A"
},
{
"__object_type": "contact",
"id": "cont_LXQqW8mvD0BbCR6qhRPbzPZF7gCbXQIw6GD8vqKipss"
}
],
"cursor": null
}More complex query
A more complicated example would be finding CEOs of SaaS companies that have at least one email address.
{
"query": {
"type": "and",
"queries": [
{
"type": "object_type",
"object_type": "contact"
},
{
"type": "field_condition",
"field": {
"type": "regular_field",
"object_type": "contact",
"field_name": "emails_count"
},
"condition": {
"type": "number_range",
"gt": 1
}
},
{
"type": "field_condition",
"field": {
"type": "regular_field",
"object_type": "contact",
"field_name": "title"
},
"condition": {
"type": "text",
"mode": "full_words",
"value": "CEO"
}
},
{
"type": "has_related",
"this_object_type": "contact",
"related_object_type": "lead",
"related_query": {
"type": "field_condition",
"field": {
"type": "custom_field",
"custom_field_id": "cf_B57sofuEB7OBneH86SJctTr7hfiAiQcgkGRbAQfha0Z"
},
"condition": {
"type": "term",
"values": ["Software as a service"]
},
"negate": false
}
}
]
}
}In this query you can see several new concepts:
- A different condition for a field that represents a
"number_range"as opposed to just textual match.gt: 1means greater than one. - A field type "custom_field" that references a Lead Custom Field by its id.
- A
"has_related"query that lets you match on data from a different related object rather than the one you want returned, in this case a Lead.
If the examples here don't cover your use case, check out Visual Query Builder for help with building a query structure tailored to your needs.
Visual Query Builder
Instead of composing the JSON query structure by hand, you can build your query visually on the Leads Page or Contacts page in Close app, and then copy the JSON query structure by clicking the triple-dot menu on the top right and selecting "Copy Filters".
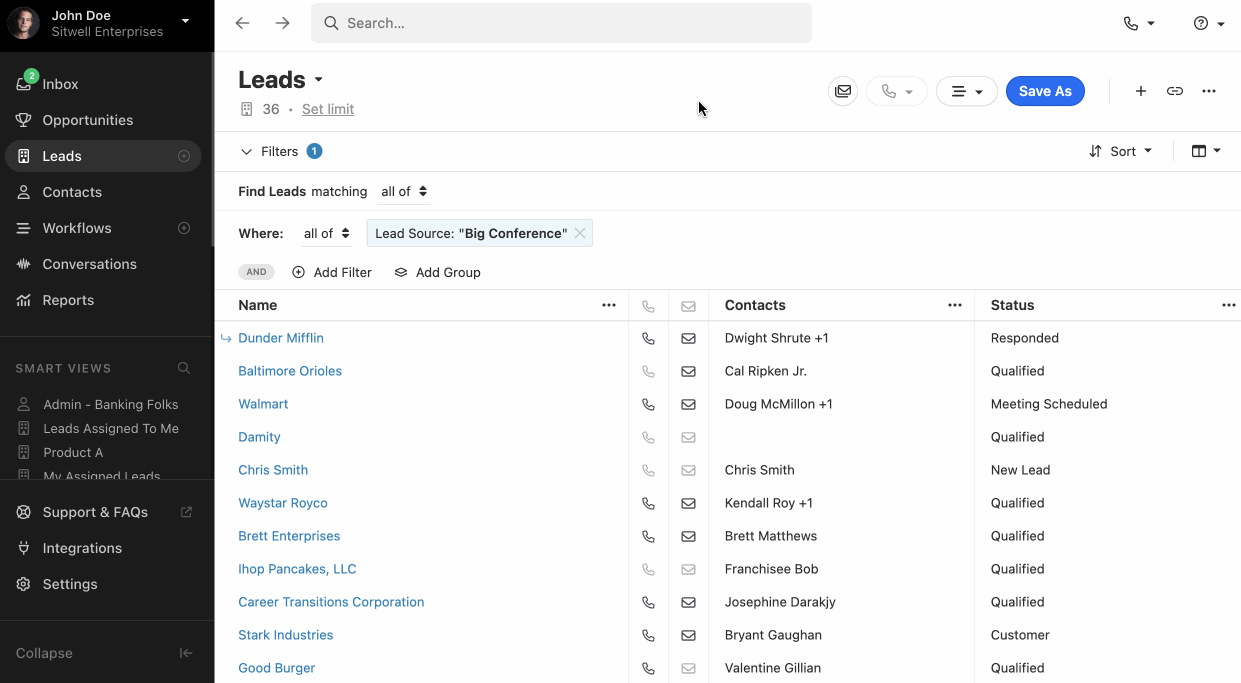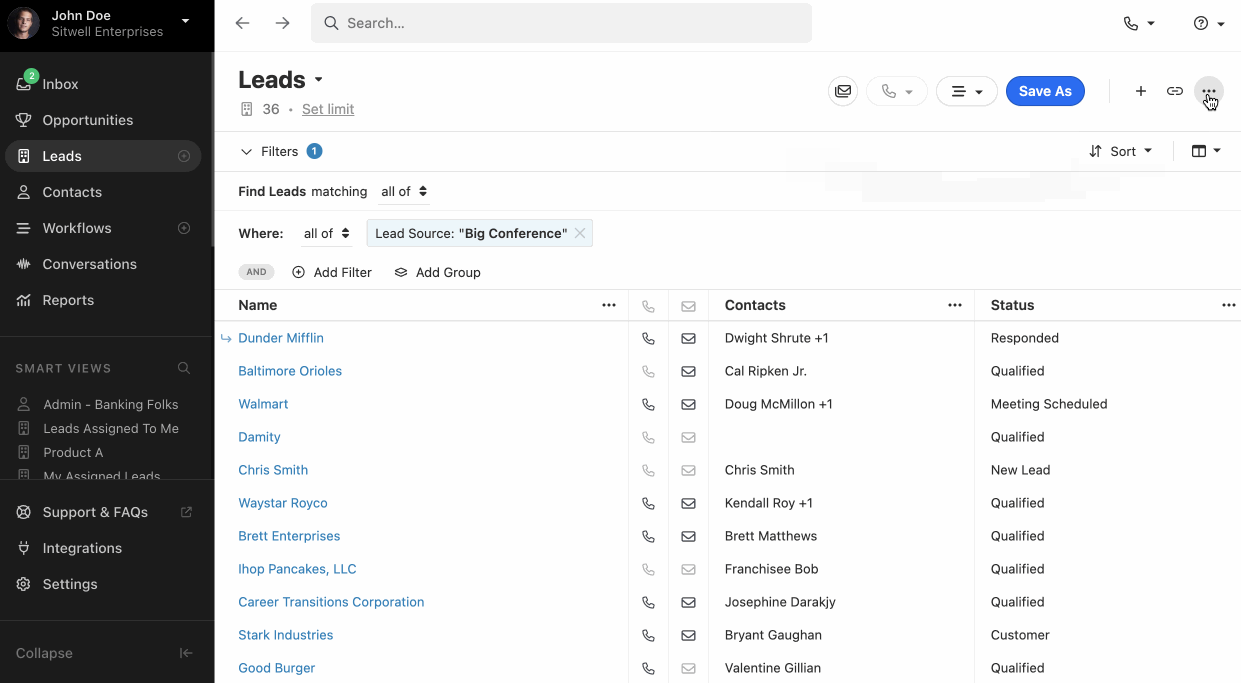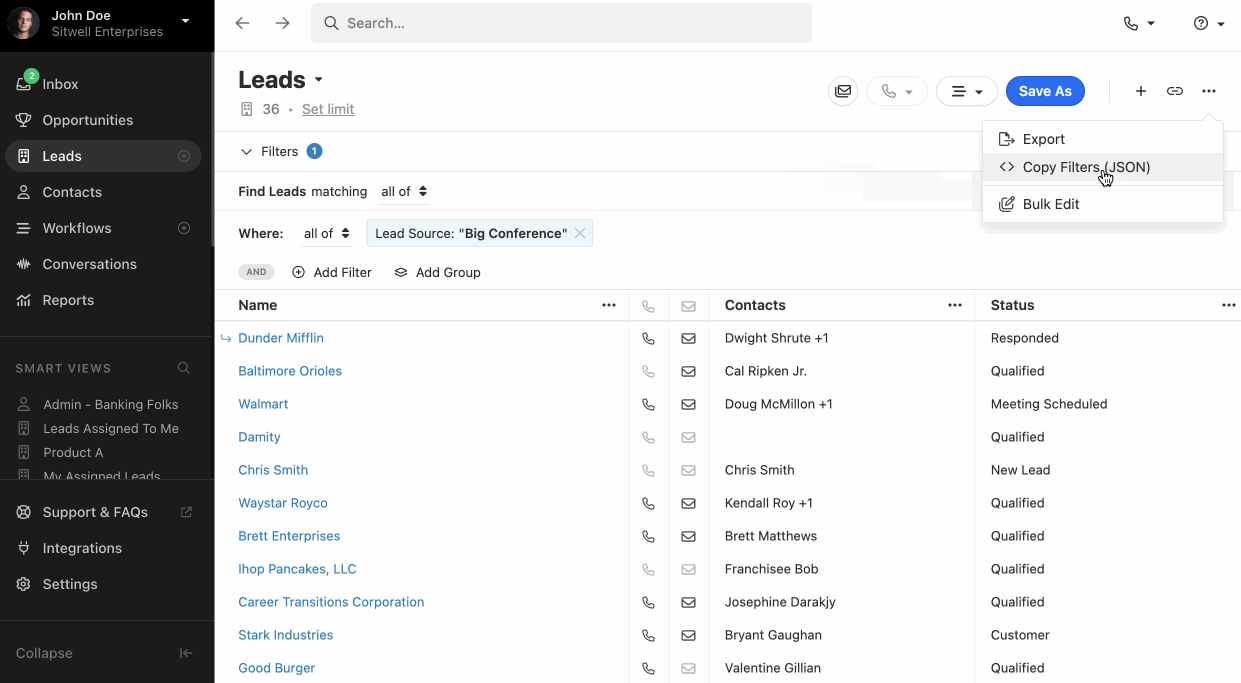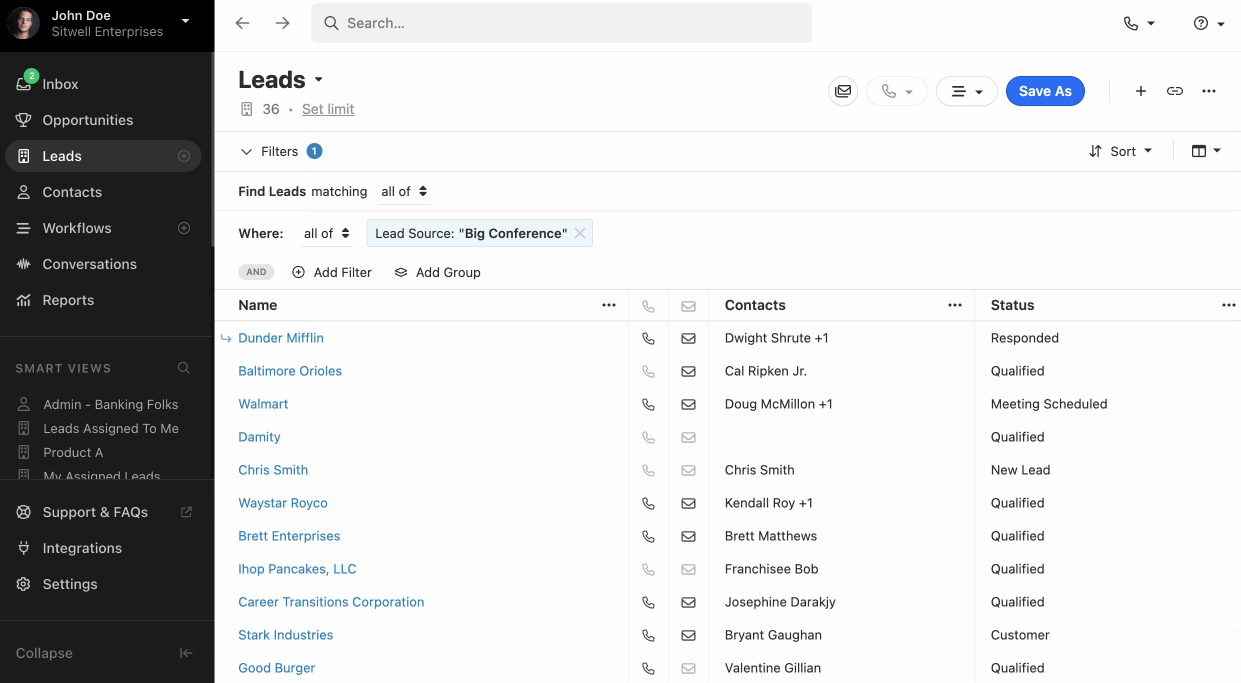
Output control
By default, the Advanced Filtering API only returns the IDs of the matched
objects to improve performance. If you want to get more the data for the object,
you will need to pass a _fields object to specify which fields you want
returned for the object you're filtering for. For example:
{
"query": ...,
"_fields": {
"contact": ["id", "name", "title"]
}
}The fields are exactly the same as ones in REST API for corresponding object types.
This results in the following:
{
"data": [
{
"__object_type": "contact",
"id": "cont_HjTcJFiNli2AKf5fioygQDVSpA9nJILI9SkKv3nBk0A",
"name": "Bruce Wayne",
"title": "The Dark Knight"
},
{
"__object_type": "contact",
"id": "cont_LXQqW8mvD0BbCR6qhRPbzPZF7gCbXQIw6GD8vqKipss",
"name": "Steli Efti",
"title": "CEO & Co-Founder"
}
]
}Results limit
If you want to only get first N results, you can specify a results limit.
Limiting results might be useful if you have 1000 objects but you want to act only on the first 100.
{
"query": ...,
"results_limit": 100,
}Note that this limits the number returned in the overall result set and is separate from pagination.
Results count
Sometimes you might want to know how many results there are. For performance,
they are not included by default. Request them explicitly with include_counts
flag.
{
"query": ...,
"include_counts": true,
}In the response, you'll get a count object.
{
"data": [...],
"count": {
"limited": 3,
"total": 3
}
}If you don't need the actual results but only care about the number, set the
results_limit to zero.
{
"query": ...,
"include_counts": true,
"results_limit": 0
}In the response, the total count is the number you're interested in.
{
"data": [],
"count": {
"limited": 0,
"total": 3
}
}Sorting
You can sort the objects returned using a sort field whose value is a list of
fields and their respective sort directions. In this example, we sort Contacts
by title.
{
"query": ...,
"sort": [
{
"direction": "asc",
"field": {
"object_type": "contact",
"type": "regular_field",
"field_name": "title"
}
}
]
}Sorting can be in either asc or desc direction.
Only numbers, dates, and text fields that belong directly to an object can be used for sorting. References/ID fields or fields from other objects cannot be used for sorting.
Pagination
A single request only returns a page worth of results. You can control how many
results you want on one page using the _limit field, and ask for the next
pages by sending the cursor field populated with a value from a previous
response.
{
"query": ...,
"_limit": 10,
"cursor": "<random string>" // <- cursor value from previous response
}When the cursor value you're received in your most recent response is null, it
means that you've reached the last page and no more results are available.
Cursors expire after 30 seconds; if you try to use an expired cursor you'll get
an Expired cursor error.
We have a hard limit of 10,000 objects when paginating. If you need to paginate
for more than 10,000 results, update your query to return smaller batches of
objects. A popular method to do this would be to use the date_created field as
a range, and make multiple requests while incrementing or decrementing the date.
Note: When paginating, be sure to use a sort that won’t change often like
date_created, so that you won’t miss any results if the sort order changes
between individual page requests.
Available query types
ID query
Matches a single object directly by its ID.
{
"type": "id",
"value": "cont_abcdef"
}Object type
Specify the object type that the API should return (i.e. contact or lead)
{
"object_type": "contact",
"type": "object_type"
}Text query
Filter for text across most text-like fields on an object.
{
"type": "text",
"value": "Bruce",
"mode": "full_words"
}The two available modes are:
full_wordssearches all specified words anywhere in the text but disregards position of the words.phrasesearches the words in specified order next to each other.
Has related
A has_related query lets you filter for a Contact based on data of the Lead
they belong to, as well as individual email address and phone number records.
{
"type": "has_related",
"this_object_type": "contact",
"related_object_type": "lead",
"related_query": {
"field": {
"object_type": "lead",
"type": "regular_field",
"field_name": "source"
},
"condition": ...,
}Query negation
All queries support negation. By specifying "negate": true, everything that
matches the query will not be returned, and everything that doesn't match
the query will.
Combining queries with AND/OR
To get objects that match multiple conditions all at once (AND) or at least one of the conditions, use and/or queries.
{
"type": "and",
"queries": [
query1, query2, query3
]
}
{
"type": "or",
"queries": [
query1, query2, query3
]
}Field Value Condition Query
Match Contacts where the value in a specific field fits the Field Condition.
{
"type": "field_condition",
"field": {
"type": "regular_field",
"object_type": "contact",
"field_name": "emails_count"
},
"condition": {
"type": "number_range",
"gt": 1
}
}There can be two field types: regular fields and custom fields.
{
"field": {
"type": "regular_field",
"object_type": "contact",
"field_name": "name"
}
}Custom fields:
{
"field": {
"type": "custom_field",
"custom_field_id": "cf_abcdef"
}
}If you're unsure what query type to use, try the Visual Query Builder.
Field Conditions
Field Conditions are conditions that apply to individual field values as opposed to entire object.
Boolean
A yes/no value.
{
"type": "boolean",
"value": true
}Current user
Represents a reference to a currently authenticated user, also known as "me".
Use with fields like created_by.
{ "type": "current_user" }Exists
Matches if the field is set to some value. Null or missing fields do not match.
{ "type": "exists" }Text
Filters for text in the field value. Similar to Text query.
{
"type": "text",
"value": "Bruce",
"mode": "full_words"
}Term
Matches one or multiple specific Enumeration or Choices values.
{
"type": "term",
"values": ["draft", "sent"]
}Reference
Matches specific object IDs in reference fields like User ID or Lead Status IDs.
{
"type": "reference",
"reference_type": "user",
"object_ids": ["user_abc", "user_def"]
}Most commonly used fields
For Contact: Object type: contact
created_by: User IDdate_created: datetimedate_updated: datetimeemails_count: integerlead_id: Lead IDphones_count: integertitle: textupdated_by: User IDurls_count: integer
For Lead: Object type: lead
addresses_count: integerall_urls_count: integercreated_by: User IDdate_created: datetimedate_updated: datetimedescription: textdisplay_name: textstatus_id: Lead Status IDupdated_by: User IDurl: url
For Contact Phones: Object type: contact_phone
type: textphone: text
For Contact Emails: Object type: contact_email
type: textemail: email address
For Contact URLs: Object type: contact_url
type: texturl: url
For Addresses: Object type: address
address_1: textaddress_2: textcity: textcountry: textlocation: textstate: textzipcode: text